Microsoft Windows Server Versions
Customers trust Microsoft to be their technology partner and have chosen Windows Server to run their businesses for decades. Join startups, governments, and Fortune 500 customers who run Windows Server on Azure and take advantage of unmatched security, the ability to operate hybrid seamlessly and achieve cost savings on the cloud that knows Windows best. According to Microsoft's August announcement, the next BizTalk Server product will contain previously released feature packs, and will support 'the latest versions of Windows Server, SQL Server. Over the past month I've been running training events for Microsoft's distribution partners on Windows Server 2019, and one of the things that was mostly kept under wraps until the product launch was the differences between the different SKUs.
Version Check is a basic operation which every developer does while building applications. Microsoft says, wrong Conditions may cause Application Compatibility issues to both developers and users, when they look at migrating the existing applications to a newer OS. The Windows version is actually composed of a bunch of different fields, all packed into an OSVERSIONINFO structure.

The relevant parts of the OSVERSIONINFO are:
- Major Version (dwMajorVersion)
- Minor Version (dwMinorVersion)
- Build # (dwBuildNumber)
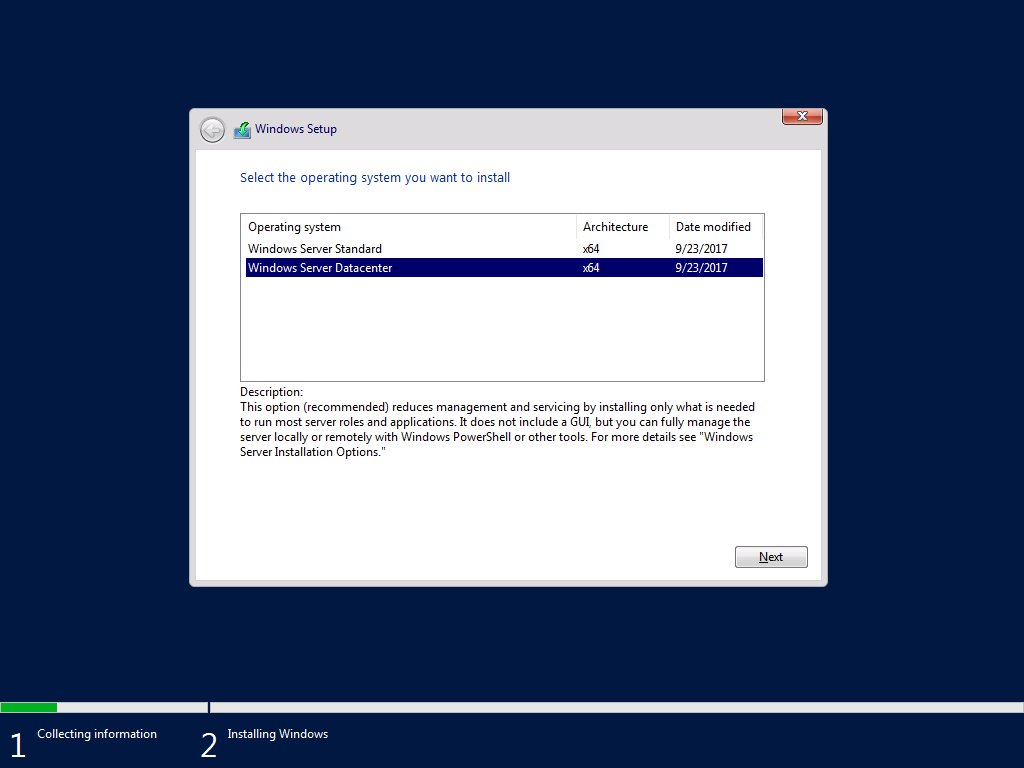
Microsoft Windows Server 2019 Versions
List of Windows Client OS with their Version Numbers
| Operating System | Version Number |
| Windows 1.0 | 1.04 |
| Windows 2.0 | 2.11 |
| Windows 3.0 | 3 |
| Windows NT 3.1 | 3.10.528 |
| Windows for Workgroups 3.11 | 3.11 |
| Windows NT Workstation 3.5 | 3.5.807 |
| Windows NT Workstation 3.51 | 3.51.1057 |
| Windows 95 | 4.0.950 |
| Windows NT Workstation 4.0 | 4.0.1381 |
| Windows 98 | 4.1.1998 |
| Windows 98 Second Edition | 4.1.2222 |
| Windows Me | 4.90.3000 |
| Windows 2000 Professional | 5.0.2195 |
| Windows XP | 5.1.2600 |
| Windows Vista | 6.0.6000 |
| Windows 7 | 6.1.7600 |
| Windows 8.1 | 6.3.9600 |
| Windows 10 | 10.0.10240 |
Yochay Kiriaty says that “A lot can go wrong when version checking is misused. A user might experience a “silent fail” where the application simply fails to load and nothing happens. Or, a user might see a dialog box indicating something to the effect of “you must be running Microsoft Windows XP or later” when in fact, the computer is running Windows 7. Many other consequences to poor version checking can inconvenience users as well.”
Reference- Windows Team Blog
Using appropriate conditions to determine the OS is a very important step to ensure App-Compatibility. For more information on Application Compatibility Operating System Versioning and Windows 7 RTM – Read Here and Here.